Vertical Farming Solutions for Enhanced Food Security
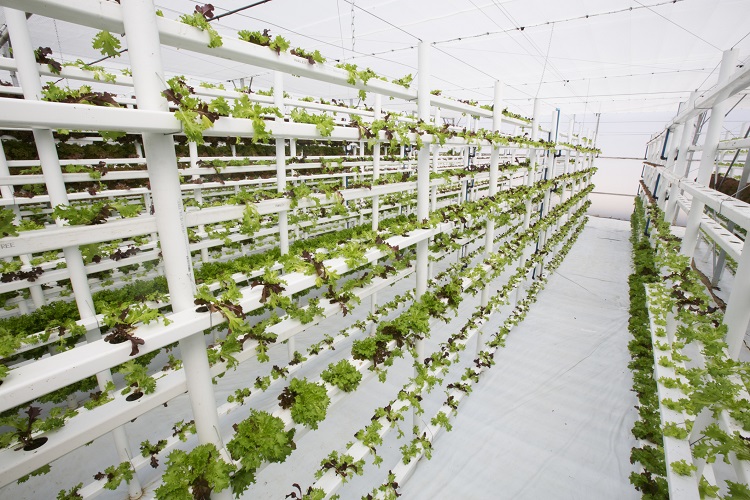
In the face of a rapidly growing global population and the challenges posed by climate change, the quest for sustainable and reliable food sources has intensified. Vertical farming emerges as a cutting-edge solution, offering a range of innovative approaches to enhance food security on a global scale. In this exploration, we delve into the transformative potential of vertical farming solutions and their role in securing a stable food supply for the future.
1. Year-Round Production: Defying Seasonal Constraints
One of the primary advantages of vertical farming in bolstering food security is its ability to defy seasonal constraints. Traditional agriculture is often subject to the limitations imposed by changing seasons and adverse weather conditions. Vertical farms, operating in controlled indoor environments, enable year-round production. This continuous cultivation ensures a stable and predictable food supply, reducing the vulnerability of communities to seasonal fluctuations and climate-related disruptions.
2. Efficient Land Utilization: Growing Up Instead of Out
Vertical farming optimizes land utilization, a critical factor in the quest for food security, especially in urbanized areas. By stacking crops vertically, these farms significantly reduce the amount of land required for cultivation. This efficiency is particularly valuable in densely populated regions where available arable land is limited. Vertical farming’s compact footprint allows for agricultural productivity in non-traditional spaces, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient food production system.
3. Water Conservation: Cultivating Sustainability
Vertical farming employs advanced irrigation methods such as hydroponics and aeroponics, drastically reducing water usage compared to traditional farming. With water scarcity becoming an increasingly pressing global issue, the water-efficient nature of vertical farming is a crucial component in achieving sustainable food security. By cultivating crops with minimal water requirements, vertical farms play a pivotal role in addressing the challenge of water scarcity and promoting responsible water management practices.
4. Localized Production: Reducing Dependency on Imports
Vertical farming promotes localized production, a key strategy for enhancing food security at the community level. By cultivating crops closer to urban centers, these farms reduce the Vertical farming system dependency on long-distance transportation and imported goods. This not only lowers the carbon footprint associated with food distribution but also enhances the resilience of local communities by creating a more self-reliant food supply chain.
5. Technological Innovation: Precision Agriculture for Maximum Yield
The integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and automation, sets vertical farming apart as a high-tech solution for food security. These technologies enable precise control over environmental factors, optimizing conditions for plant growth and maximizing yield. The data-driven approach of vertical farming allows for real-time monitoring and adjustments, ensuring efficient resource utilization and consistent crop production.
In conclusion, vertical farming solutions stand at the forefront of the quest for enhanced food security. By defying seasonal limitations, optimizing land use, conserving water, promoting localized production, and leveraging technological innovation, vertical farming presents a multifaceted strategy to meet the growing demand for a reliable and sustainable food supply. As we navigate the complexities of a changing world, vertical farming emerges as a beacon of hope, offering tangible solutions to address the critical issue of global food security